|
The following results are parts of the RITE in-house R&D on CO2 ocean sequestration. |
|
| Research on the Mitigation Effect on Surface Ocean Acidification by CO2 Ocean Sequestration Research on Deep-sea Organisms Food Webs to Develop the Methodology for Predicting Ecosystem Impact |
|
|
Research on the Mitigation Effect on Surface Ocean Acidification by CO2 Ocean Sequestration 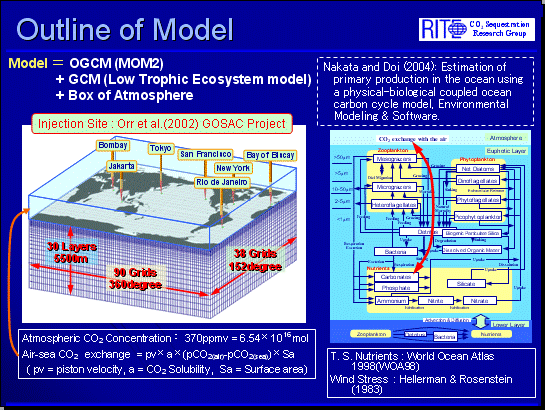 Outline of global numerical simulation model Global numerical simulation model is constituted by physical model and ecosystem model. The physical model used in this study is Version 2 of the GFDL Modular Ocean Model (MOM2; Pacanowski, 1996). The ecosystem model is lower-trophic marine ecosystem model (Nakata and Doi, 2004). The result of the
simulation suggested causing the acidification in the mid and deep
layer corresponding to the amount of CO2 sequestration. It suggested that CO2 ocean sequestration could decrease the acidification in the ocean surface.
The condition of CO2 ocean sequestration to restrain both a surface and a mid and deep layer
acidification seems to be clarified according to a current research.
|
|
Research on Deep-sea Organisms Food Webs to Develop the Methodology for
Predicting Ecosystem Impact 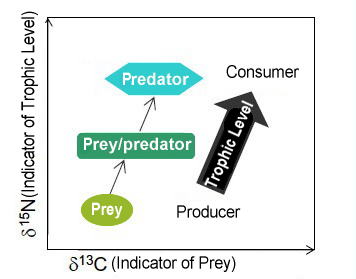
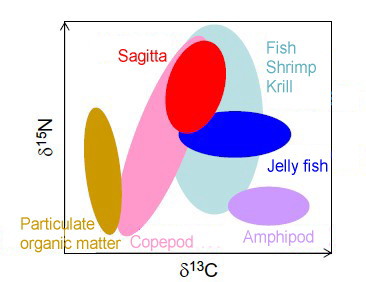
Above schematic shows the food web structure of the research area. This result contributed to develop a deep-sea ecosystem model. |