| Fig. 2 Ocean CO2 Sequestration Feasibility in Terms of Global Carbon Balance |
|
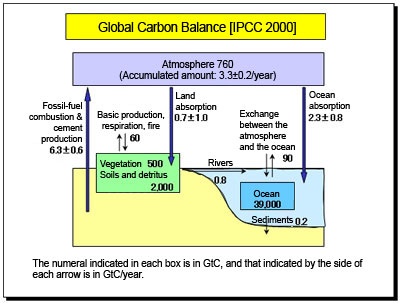
The feasibility of ocean CO2 sequestration technology is described in the following in terms of global carbon balance.
The annual emissions from fossil-fuel combustion into the atmosphere is 6.3 GtC (6.3 Giga tons of carbon), of which 0.7 GtC is absorbed into the land, 2.3 GtC into the ocean, and 3.3 GtC remains in the atmosphere causing a gradual increase in greenhouse gases. The idea of the Ocean CO2 Sequestration Project is to artificially dissolve and dilute part of the remaining 3.3 GtC in the ocean.
Since 39,000 Gt of carbon is contained at intermediate depth in ocean water, the impact on the marine environment of a carbon increase of several Giga tons per year may be negligible. The ocean provides a far larger carbon storage capacity than does land vegetation. For Japan, which is surrounded by the sea, ocean CO2 sequestration is assuredly a vital and useful technology worthy of development for the future. |

