- Home
- Development Themes : Advanced development of CO2 capture by solid sorbents
Development Themes
Advanced development of CO2 capture by solid sorbents
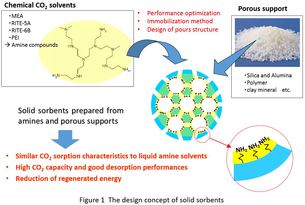
Solid sorbents prepared from amines and porous supports exhibit similar CO2 sorption characteristics to liquid amine solvents. Additionally, these solid sorbents have the advantage of requiring lower heat input during regeneration processes. For this reason, RITE has developed new solid sorbents using novel amine compounds (Figure 1).
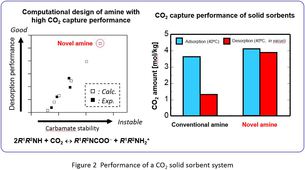
During this development work, the relationship between amine structures and their CO2 desorption performances was established based on computational chemistry. The results led to the fabrication of a new solid sorbent exhibiting greater efficiency in terms of desorption performance and sorption capacity (Figure 2).
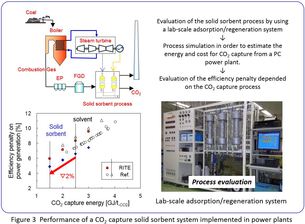
RITE has also conducted simulation studies to accurately estimate the energy requirements and cost of CO2 capture from coal-fired power plants (Figure 3), using models based on the application of amine–CO2 chemical reactions. The energy efficiency of a power plant with a CO2 capture system was estimated to improve by approximately 2 % when a solid sorbent was used in place of an advanced liquid amine solvent.
Currently, we are evaluating the solid sorbent process using a lab-scale adsorption/regeneration test apparatus, and also carrying out simulation studies on the resulting efficiency penalty with regard to power generation. These studies are meant to establish the practical applicability of the RITE-developed solid sorbent.
Click images to enlarge.